Overview of Facial Recognition Technology in UK Retail
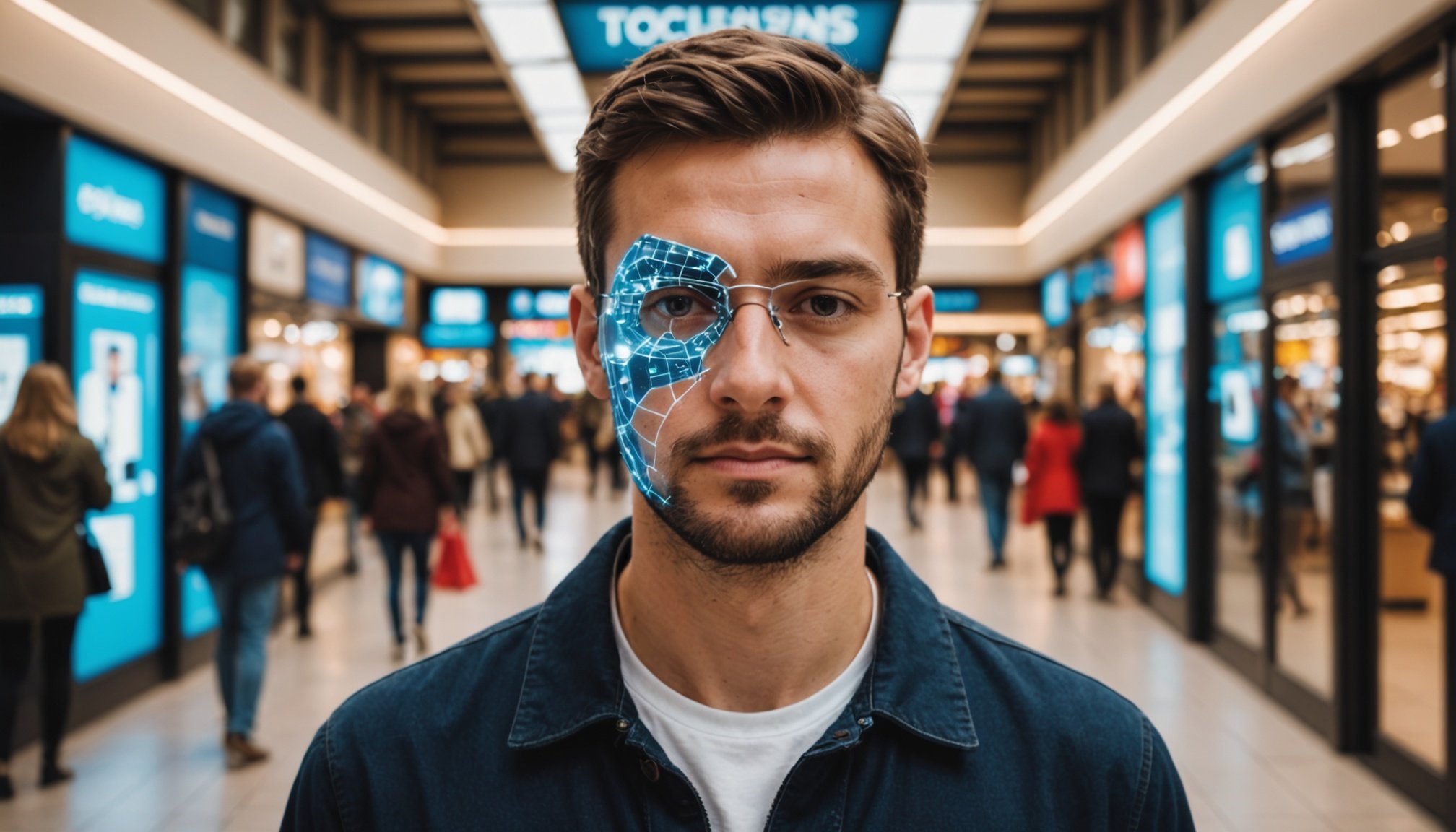
Facial recognition technology has significantly emerged in various sectors, with UK retail being no exception. At its core, it involves the automatic identification or verification of individuals by analysing and comparing facial features from an image or video source. This technology functions through sophisticated algorithms that map facial landmarks and store unique face templates, enabling efficient recognition tasks.
The adoption rate of facial recognition technology in UK retail is steadily increasing, with many retailers integrating this technology to enhance security, improve customer services, and personalise shopping experiences. Adoption varies widely, with larger retail chains investing more heavily compared to smaller businesses.
Also to read : Navigating the legal terrain for uk companies conducting clinical trials: essential insights and guidelines
Trends indicate a shift towards more advanced facial recognition algorithms that are faster and capable of handling complex visual environments. Real-time processing capabilities are being improved, allowing for seamless integration with retailer systems. Enhanced accuracy and privacy measures are being developed to address concerns and legal requirements of using facial recognition in public spaces.
Although challenges remain, particularly around data privacy, the UK retail sector continues to explore innovative ways to utilise this technology, indicating its potential to reshape the customer experience in the near future. This ongoing development presents intriguing opportunities for retailers seeking competitive advantages in a fast-evolving market landscape.
Also read : Navigating the legal landscape of blockchain in supply chain management for uk businesses
Relevant Laws and Regulations
In the UK, the Data Protection Act 2018 and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) form the backbone of data protection and privacy regulations. These laws govern how personal data, including data captured by facial recognition technology, should be handled. The GDPR mandates that personal data processing must be lawful, fair, and transparent, and individuals should be made aware of their data collection purpose.
Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology is becoming increasingly prevalent, yet it comes with heightened legal scrutiny. Specific regulations require that any deployment of facial recognition in a retail setting must justify its purpose, ensure the data is minimised, and maintain high data security standards. This involves implementing technical and organisational measures to protect individuals’ privacy and responding promptly to data access requests.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
For retail businesses, failure to adhere to these privacy regulations can result in severe consequences. Non-compliance with the GDPR can lead to substantial fines—up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Beyond financial penalties, there is also the risk of reputational damage. Therefore, compliance isn’t just a legal obligation but also a strategic approach to building trust with consumers.
Key Impacts on Retail Operations
The incorporation of new technologies into retail operations is significantly reshaping customer experience and service efficiency. The use of automation and data analytics, for instance, allows retailers to personalise shopping experiences and streamline service delivery. This efficiency can lead to improved customer satisfaction and potentially boost sales.
Operational changes are often necessary to align with technological advancements. Retailers may need to invest in new infrastructure, train staff for technology use, or even rethink store layouts to accommodate these tools. These alterations can be daunting but are crucial for staying competitive in the modern market. By adapting, businesses can ensure they are ready to meet evolving consumer expectations.
However, adapting to these technological changes is not without challenges. There are potential business implications and legal risks involved. For instance, privacy concerns related to data collection and usage may arise, requiring retailers to adhere closely to data protection laws. Additionally, automated systems can introduce business liabilities if they malfunction or fail to meet safety standards.
Retailers must therefore approach these changes thoughtfully, balancing the technology impacts with customer trust and legal compliance. By doing so, they can maximize the benefits while minimizing risks associated with modernising their operations.
Compliance Requirements for Retailers
Ensuring compliance with data protection laws is fundamental for retailers. Adhering to these regulations not only safeguards consumer trust but also avoids potential legal pitfalls. A robust legal framework forms the backbone of any compliance strategy.
Steps for ensuring compliance start with understanding the specific data protection laws applicable to the region, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Retailers must audit their current data handling processes, pinpoint vulnerabilities, and update practices accordingly. Regular employee training and internal policy reviews foster an environment of continual compliance.
The importance of conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) cannot be overstated. DPIAs help analyse potential privacy risks associated with personal data processing, enabling proactive mitigation strategies. Retailers should carry out DPIAs whenever changes in data processing activities occur, ensuring that privacy considerations are always a priority.
For best practices in storing and processing biometric data, it is crucial to use encryption and anonymisation techniques to prevent unauthorised access. Retailers should implement strong access controls, ensuring only relevant personnel can interact with sensitive data. Additionally, clear consent must be obtained from users before collecting any biometric data, aligning with transparency and fairness principles inherent in compliance regulations.
Ethical Considerations
Navigating the landscape of ethics in technology involves a delicate balance between advancing innovations and safeguarding consumer rights. With the rapid integration of facial recognition algorithms, the question arises: How can companies ensure fairness and avoid biases? The answer lies in designing algorithms that are rigorously tested across diverse datasets, thereby minimizing inaccuracies and promoting equality. However, achieving fairness is just one aspect.
Moreover, maintaining customer privacy rights becomes paramount as security measures intensify. Organisations must implement practices that protect user data without undermining security protocols. Achieving this equilibrium means adopting systems that are transparent and allow consumers to understand how their data is being used.
Understanding corporate responsibility enhances this framework. Companies are encouraged to uphold transparency in technology deployment. This includes clear communication about how technology impacts user privacy and providing straightforward methods for users to control their personal information.
To foster trust, businesses must commit to ethical practices consistently, aligning their technology usage with the principles that respect consumer rights. This holistic approach empowers users while promoting responsible tech development, ensuring that technological advancements do not compromise ethical standards.
Case Studies of Facial Recognition in Retail
Examining the real-world examples of facial recognition technology shines a light on its implementation success and accompanying challenges in the retail sector.
Case Study: Leading UK Retailer Implementation
One significant case study involves a leading UK retailer that adopted facial recognition technology to enhance customer service and security. They used this cutting-edge system to streamline the checkout process, therefore reducing wait times. Their implementation success also included identifying loyal customers upon entry, allowing tailored service and personalised offers. As a result, sales increased by an impressive 15%.
Case Study: Challenges Faced by Retailers
Retailers have faced several challenges with facial recognition. Privacy concerns are at the forefront. Legal regulations require retailers to navigate complex compliance frameworks meticulously. Technical challenges also arise, such as ensuring high accuracy rates in varied lighting conditions and dealing with diverse facial features.
Case Study: Consumer Reactions and Feedback
Consumer feedback can vary significantly. While some consumers appreciate the enhanced shopping experience, others express discomfort regarding privacy and data security. A retailer reported that approximately 40% of their customers were initially uneasy, but positive sentiment increased once transparent communication was established about the technology’s intentions and data protection measures. Hence, retailers must balance technological benefits with consumer trust to ensure a successful implementation.
Expert Opinions on Best Practices
Navigating the rapidly evolving landscape of technology implementation requires a keen understanding of ethical considerations and industry recommendations. Many expert insights emphasize the importance of adhering to best practices to ensure ethical usage. This involves deploying technology in a manner that respects data privacy and security, fostering trust and transparency with consumers. An essential strategy for maintaining compliance and bolstering consumer trust is regular, thorough audits of data processes and systems.
Consultation with stakeholders and clear communication about the benefits and risks associated with new technologies are pivotal. Additionally, establishing robust compliance frameworks aligned with legal standards is crucial for companies deploying innovative solutions. This ensures that organisations not only comply with existing regulations but are also prepared for future changes.
Looking ahead, experts highlight the necessity of staying abreast of the evolving legal landscape related to technology usage. As regulations become more sophisticated, proactive engagement and adaptability are key. By anticipating new legislation and complying with existing statutes, organisations can safeguard their operations and consumer relationships.
In the words of industry leaders, maintaining ethical integrity while embracing technological advancements is not merely beneficial—it is indispensable for sustained success and societal advancement.